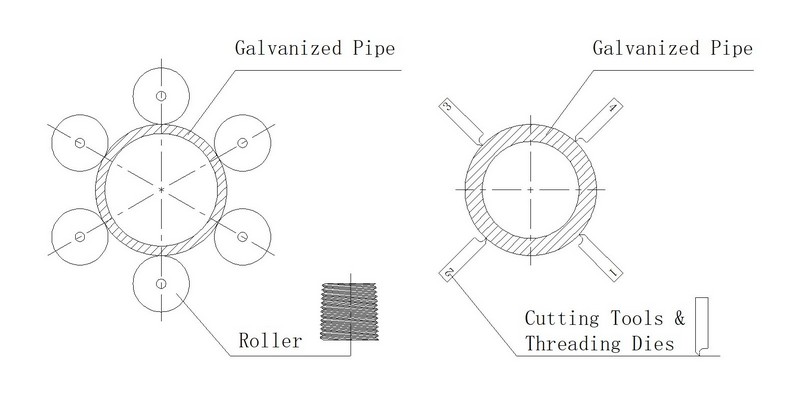
|
No |
Category |
Cutting |
Rolling |
Annotation |
|
1 |
Cooling oil consumption |
100% |
50%~70% less than the cutting |
With the improvement of urban environmental protection and garbage classification requirements, the recovery cost of lubrication/cooling oil and metal scraps generated by the lathe cutting machine will increase, especially the treatment of the scraps containing zinc will become more and more stringent, and the treatment cost will increase significantly. |
|
2 |
Metal scarps |
100% |
There are no metal scraps during thread forming |
|
|
3 |
Waste disposal |
Need |
Don't need |
|
|
4 |
The thread section is |
Significantly resulting in a decrease in the strength of the steel pipe thread section/surface hardness /its roughness |
Little, the thread has a cold hardening effect |
The work caused by shear deformation during cutting and the work caused by the friction in front and back of the tool is transformed into heat similar to the annealing treatment of the steel pipe, and the surface hardness and quality of the steel pipe thread section are reduced a lot |
|
5 |
Surface Burr of thread |
A lot |
None, the surface is smooth, similar to grinding |
Cutting is point-to-point contact between the tool and the steel pipe, and rolling is line-to-line contact to form the thread profile |
|
6 |
Defective threads |
On-site production, it is easy to make the thread offset, a missing, thin or broken thread which is unacceptable |
Fully comply with the BSPT and NPT National Standard and achieve zero defects on-site scale production |
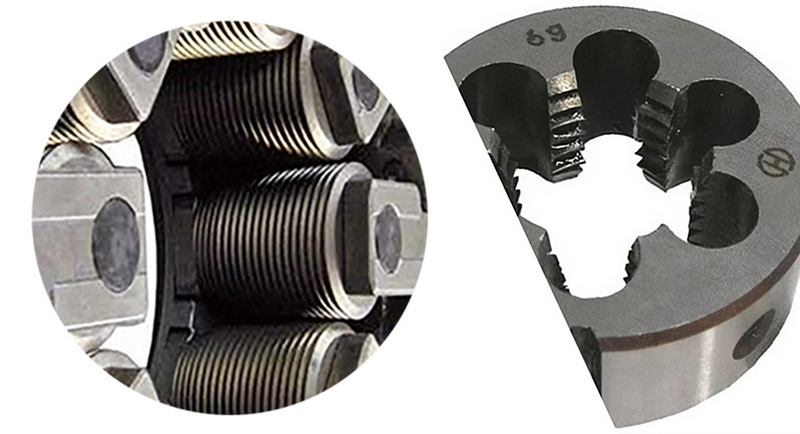
Rolling is a well-established non-metallic processing method that uses two or more rolling wheels to extrude steel pipes at room temperature, generating parallel threads or 1:16 taper threads. This process does not produce any metal waste and the surface shape of the rolling wheel perfectly matches the finished shape of the workpiece, making it a mirror image-forming technique. Compared to thread-cutting methods, it offers superior dimensional stability, mechanical strength, and production efficiency. |
|
7 |
Tool taper adjustment |
For tool wear, taper adjustment is required and the accuracy depends on the operator's adjustment /experience |
No adjustment is required, the over-10K- thread-life-time conical roller is closed back and extruded to form taper threads |
During lathe cutting, the edge, front, and back of the tool wear and heat are not uniform, resulting in the constant change of taper and tooth shape affecting the thread quality |
|
8 |
Tool change |
The tool life is short. After 100~1000 threads are made the lathe cut tool must be changed to keep the quality |
The lifetime is, at least 10~100 times, more than the life of lathe cutting tools, the conical rollers can continuously produce 10,000 to 50,000 threads |
The pipe thread-cutting tool life is generally 50~200 threads, The best one of thread cutting tool life is generally 1000 threads |
|
9 |
Noise |
>>80dB |
Generally, less than 50~60 db depending on the machine speed |
The harsh metal friction noise disturbs the environment of operators and surrounding residents |
|
10 |
The soldering seam of welded pipe |
The application of the pipe thread rolling process |
Ensure that the soldering quality of each welded pipe meets the requirements of the National Welded Pipe Flattening Test Standard |
|